What factors contribute to global winds? Identify areas where winds are weak.​
The Brusk Answer:
The ocean covers about 70% of Earth'due south surface. So, it'southward not surprising that information technology plays a large part in Earth'southward environment. As Earth warms, water in the bounding main soaks up free energy (heat) and distributes it more evenly beyond the planet. The ocean also absorbs carbon dioxide from Earth's atmosphere. The additional estrus and carbon dioxide in the bounding main tin can alter the surroundings for the many plants and animals that live at that place.
Why is the ocean important for life on Globe?

The Bahamas seen from the Space Shuttle STS-52 in November 1992. Credit: NASA
The body of water is important because it is a very big part of our planet. In fact, it covers 70% of Globe's surface. The sea is a habitation and nutrient source for countless fish, mammals, plants, birds, and more than.
The body of water plays an of import role in whatever happens in our environment on Earth. Fifty-fifty if you live on land – like humans do – you wouldn't survive without the body of water!
One example: without the ocean, World would be much hotter than it is right at present. That's because the body of water absorbs rut from the Sun and spreads it more than evenly around our planet.
How does the bounding main soak upwardly oestrus from the Dominicus?
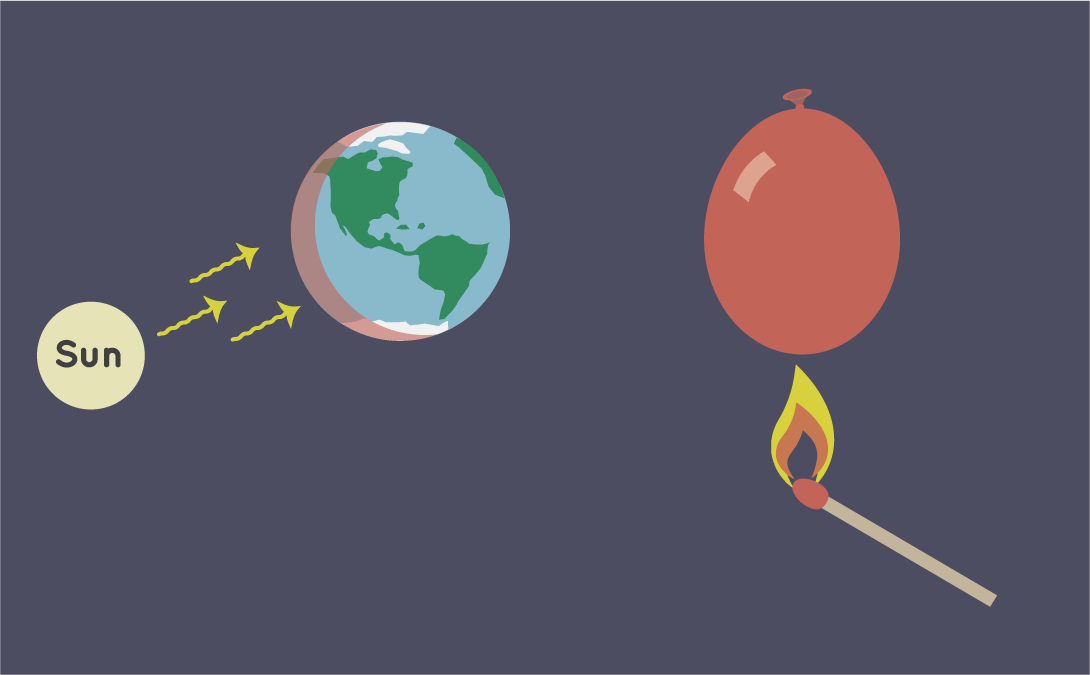
Globe's oceans help to absorb extra estrus from the atmosphere because water is practiced at storing heat. How do you think a balloon filled with water would react to a flame differently than a balloon filled with air? Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Water is excellent at storing heat. H2o has a high heat capacity—it absorbs a lot of heat before information technology begins to get hot. Air, on the other hand, is not so great at storing oestrus.
Earth's climate is warming due to human being activities. As Globe experiences a warming climate, we experience hotter air temperatures. The ocean does an excellent job of arresting the extra heat from the atmosphere, delaying the full impact of global warming.
The top few meters of the sea store equally much heat as Earth's unabridged atmosphere. So, every bit the planet warms, information technology's the ocean that gets most of the extra energy. More than 90% of the global warming is going into the ocean.
But if the ocean gets too warm, and so the plants and animals that alive there can get ill or even die.
How can a water airship teach us about climate change? Watch this video and notice out!
How are coral reefs affected by climate change?
Coral reefs are created by living creatures. Warming oceans caused by climate change are putting coral reefs in danger. Coral reefs are made by very delicate colonies of organisms that build skeletons around themselves.
Coral lives together with a certain kind of colorful algae. The algae make food using sunlight ¬– a process chosen photosynthesis. The algae share the food with the coral, and in turn, the coral gives the algae a safe and comfy place to alive.
The two of them get along fine, living in clean, clear, shallow waters where the Sun shines through brightly. Fish and other bounding main creatures dearest coral too, because there are lots of nooks and crannies for them to hibernate in.
But the algae cannot carry out photosynthesis in water that is besides warm. The algae either dice, or the coral spits it out. It's bad for the algae, the coral and the fish, because the coral lose their food sources and get weak and can die. This event is chosen coral bleaching, and it is a very serious problem in many ocean ecosystems around the world.
Read about what it's similar to be an body of water scientist studying coral reefs.
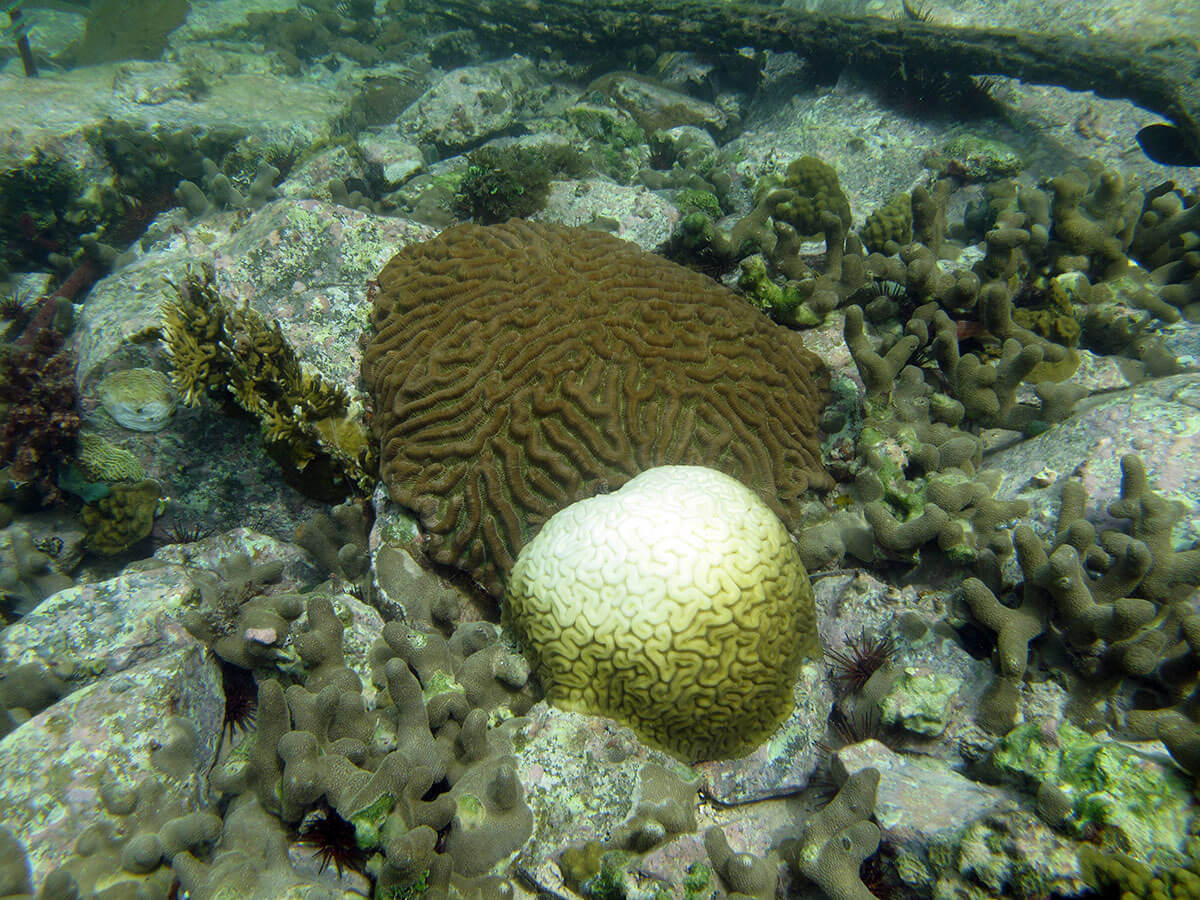

A bleached coral adjacent to an unbleached coral. Credit: Carolina Rogers/USGS
How does the ocean soak up CO2?
Fish and other animals in the bounding main breathe oxygen and requite off carbon dioxide (CO2), just like land animals. Ocean plants accept in the carbon dioxide and produce oxygen, merely like country plants. The ocean is keen at absorbing COii from the air.
However, a lot of CO2 comes from human activities, also. For example, exhaust from cars, planes, and factories put extra carbon dioxide into our air. Too much carbon dioxide in the air is a problem, as information technology causes the Earth to trap more than oestrus. The ocean absorbs near ane-quarter of the CO2 that humans create when we burn fossil fuels (oil, coal, and natural gas).
Too much carbon dioxide in the ocean causes a problem called sea acidification. You can read this article to learn all most sea acidification and its furnishings.
How does the ocean affect the climate?
The bounding main absorbs heat from the Sun and ocean currents move that warm water all around the planet. Ocean currents are like highways that carry water around the world. Heat (along with salt) is a major source of power for ocean currents.
Common cold water near the N and South Poles sinks deeper into the sea. Water near the equator is warmed past the Sun. Then, the warm surface water moves closer to the poles where it cools and sinks.
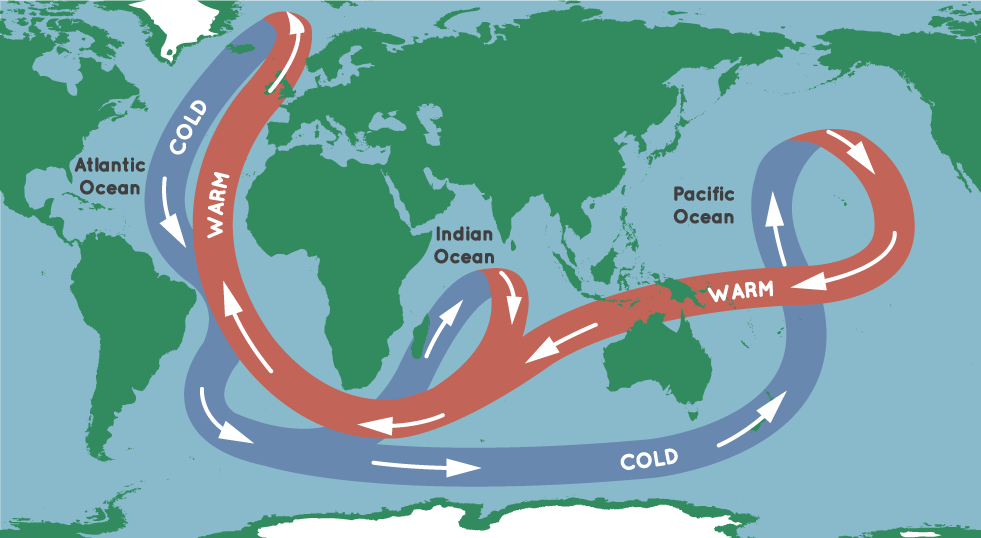
The "great ocean conveyor belt" refers to the major ocean currents that move warm water from the equator to the poles and common cold water from the poles dorsum toward the equator. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Equally Earth'due south climate warms, the h2o also warms melting body of water ice. This warming could make the h2o less cold and less likely to sink. Without sinking cold h2o, the ocean currents could tiresome downwards or stop in some places. This could modify the climate in places similar Europe that have milder climates thanks to the warm currents in the oceans around them.
Does the salt in the body of water exercise anything?
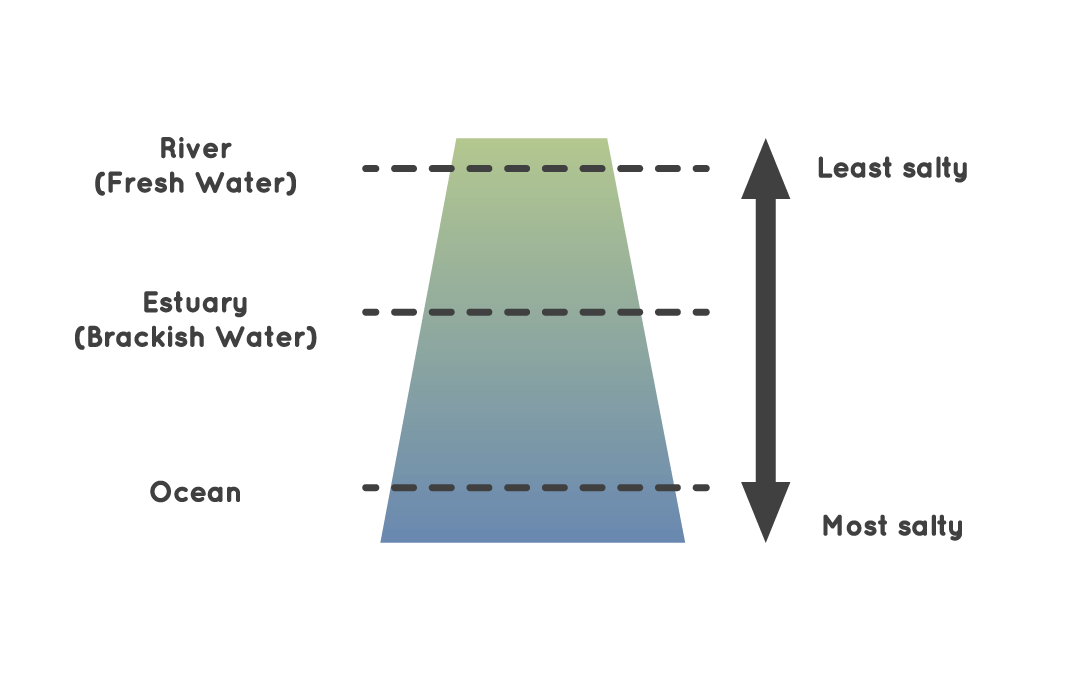
Fresh water has lower salinity (saltiness) than estuary h2o, where the body of water water mixes with river water. The bounding main itself is the nearly salty of all. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
The corporeality of common salt in the ocean also affects currents. Saltier water is heavier than less salty water. When salty body of water h2o freezes, the water ice tin can no longer agree on to the salt. Instead, the salt mixes with the h2o beneath making it saltier and heavier. Glaciers, state ice and icebergs are made of fresh water, then what happens when this water ice melts? Skilful question!
The water in the North Atlantic sinks because information technology's cold, but as well considering it's salty. Being both common cold and salty makes it actually dense and heavy, so it can sink very far. But if too much ice melts in the North Atlantic, the water could become less salty and bear on ocean currents. NASA satellites are keeping a shut heart on the melting ice, the ocean currents, and ocean life to improve understand this complicated system.
Play Become With the Menstruation to use temperature, salinity, and ocean currents to find treasure!
How does climate change impact sea level?
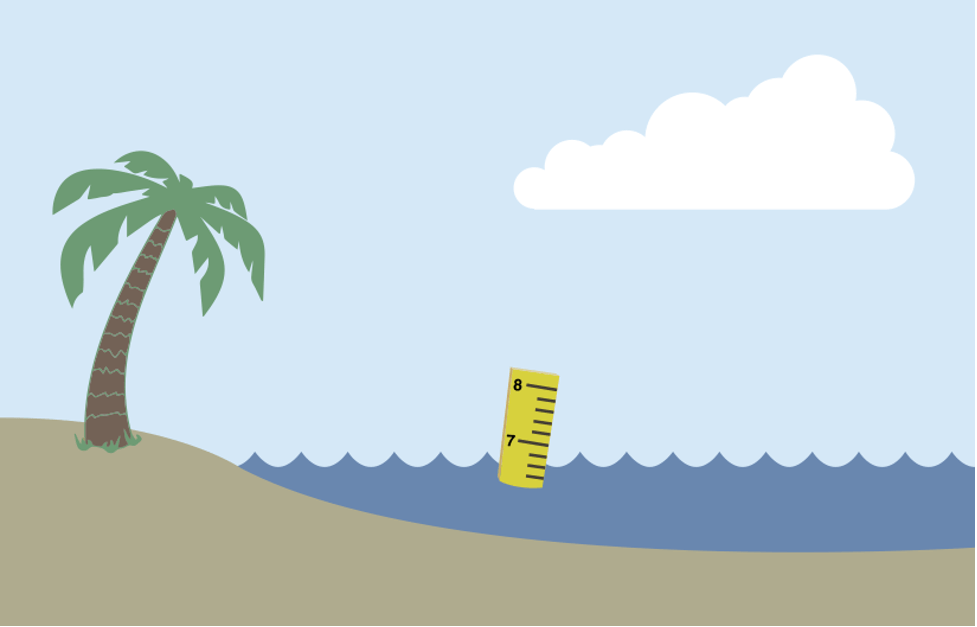

As World warms, sea levels are ascension. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Every bit Earth warms, NASA has observed that sea levels are rising. Water expands as information technology gets warmer. So, warm water takes up more room in our oceans, and this leads to higher sea levels. Another reason that oceans are rising is due to melting ice on land. Glaciers and ice sheets are large masses of water ice that sit on the land. As our planet warms, this water ice melts and flows into the oceans. More water in the oceans makes sea level college.
NASA satellites are constantly measuring sea level around the globe. Acquire more about how we mensurate sea level with satellites.
Related NASA Missions

Airborne

Aqua
ICESat-2
Jason-3
OSTM (Jason-2)

Sentinel-half-dozen Michael Freilich

Suomi-NPP
Terra
Source: https://climatekids.nasa.gov/ocean/
0 Response to "What factors contribute to global winds? Identify areas where winds are weak.​"
Post a Comment